The Greenhouse Effect
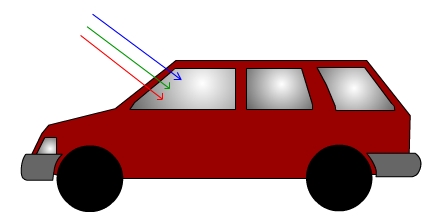
- Car windows are designed to pass visible radiation for safety reasons.
- It turns out that most glasses do NOT pass IR radiation.
- So, visible light from the 5200K Sun passes through the windows and is absorbed
by the black leather interior of the car. The leather heats up to around 350K and radiates:
- X-rays?
- Visible Light?
- IR radiation?
- Since the glass is opaque to IR radiation, the energy in the original visible radiation
gets trapped in the car and it gets hot in there!
The greenhouse effect doesn't just apply to your car, but to the entire Earth as well!

- The Earth's atmosphere is alot like a glass window.
- When it's not cloudy, it is transparent to visible light radiation.
- Some of the molecules in the atmosphere Absorb IR radiation - specifically
CO2.
- Just like the case of the car's interior, much of the visible
light radiation from the Sun is absorbed by various things at the
surface of the Earth. These things heat up and reradiate E-M radiation
appropriate to their temperature. The temperature of the Earth is
around 250K and its radiation spectrum peaks at around 11 µm. Some
of this radiation is trapped by the CO2 in the atmosphere and there is
a net heating. As the CO2 content of the atmosphere goes up because
of fossil fuel burning and deforestation, the amount of incoming
radiation doesn't change, but the amount of trapped outgoing IR radiation
increases. This is the cause of global warming. Is it happening? You bet.
Why is the Sky Blue?

- If you look towards the Sun in the sky, it appears white-yellow.
- If you look away from the Sun, since there is no light source in that
direction, you might expect the sky to be black.
- The reason it is not black is because of scattering of photons in
the upper atmosphere, mostly by molecules.
Why does the Sun look red at sunset?
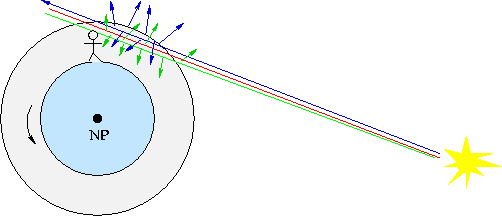
- The long pathlength through the atmosphere when the sun is low means lots of blue
and green photons get scattered out of the line of sight - leaving only the red light.
One more interesting sidelight...
Because of the gradient in the atmosphere's density, it acts like a prism.
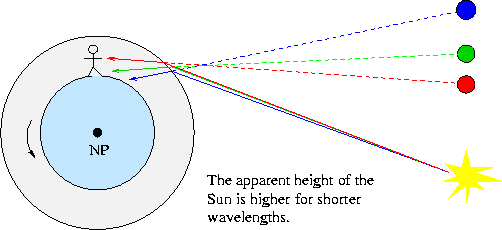
- Red light is less "bent" than green or blue light so the "red"
Sun sets first, followed by the "green" Sun, then the "blue"
Sun. When the Sun is low on the horizon, all the blue light gets
scattered out, so, the last thing you see is a "green flash".
- When you see the Sun hit the horizon, it is already a full solar
diameter below the horizon.





