- In the late 1800's various clever experiments were made to
measure the speed of light in different reference frames. The
remarkable fact began to emerge that the speed of light
is independent of the velocity of the source or the observer
(don't get this confused with the Doppler shift).
This is very surprising and counter-intuitive.
You can never catch up to a photon. Imagine two rocket ships,
one flying toward the Sun at nearly the speed of light, one away
from the Sun at nearly the speed of light. Ask them to measure
the speed of the photons streaming away from the Sun and they
measure the same 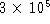 km/sec. This is not at all what
happens when considering relative velocities of cars on the
freeway.
km/sec. This is not at all what
happens when considering relative velocities of cars on the
freeway.
- Einstein took this premise, that the speed of light is independent
of reference frame, and looked to see where it led.
- This is in reality a pretty long story, but the short version is that
the constancy of ``c'' can be explained by postulating that the lengths of
Metersticks and speeds of Clocks are
 in
different reference frames.
in
different reference frames.
This is a radical concept!
- As you speed increases, your watch SLOWS DOWN! This is called
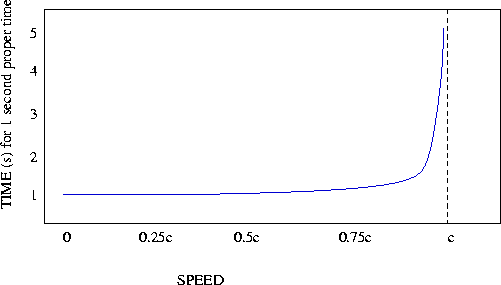
- As you approach the speed of light, the factor v/c approaches
1 and the denominator of the equation approaches 0. When you divide
anything by zero the result is
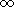 - so time essentially grinds
to a halt as you approach c.
- so time essentially grinds
to a halt as you approach c. - Q. Suppose you compare your watch to the watch of your friend
on a rocketship moving at 98% of the speed of light. Suppose you observe
a phenomenon for 1 second by your watch, how long would our friend measure
for this same event?
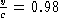
So, time is stretched out by a factor of 5 for your friend in the
rocketship. His/her clocks run at 1/5 the speed of yours.
- In the same way the length of measuring sticks decreases with
speed - this is called Length Contraction. A ruler of length
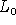 at rest, when held perpendicular to the direction of motion
will have a length:
at rest, when held perpendicular to the direction of motion
will have a length:
So, your friend at 0.98c will have a 1-foot ruler that looks like it is
only 2.4 inches long to you.
- It turns out that Mass also varies with velocity. Mass increases
with velocity in the same way that time increases::
- These things conspire to make it impossible for objects
with mass to ever exceed the speed of light - as you approach
c, the required fuel to accelerate a little faster goes up
as the mass increases toward infinity AND time slows and slows
until you never reach the last instant when you reach c.
- Could any of this possibly be true?
There have been many experiments, mostly on
elementary particles moving near the speed of light in accelerators
that have directly measured the increases of mass, dilation of time
and contraction of space. Other experiments have compared the time
passage on very accurate clocks while moving in airplanes in the
opposite directions. Even the discovery of cosmic rays was made possible
by the fact that the half-lives of the particles was effectively extended
by time dilation long enough for the particles to reach the surface of
the Earth.
- The ideas Einstein got from Special Relativity - that
rulers and clocks and mass could be affected by motion - he next
applied to gravity.
He got away from the idea of a force and instead
looked at an interpretation of gravity in terms of its effect on
space and time.
![]() km/sec. This is not at all what
happens when considering relative velocities of cars on the
freeway.
km/sec. This is not at all what
happens when considering relative velocities of cars on the
freeway.
![]()