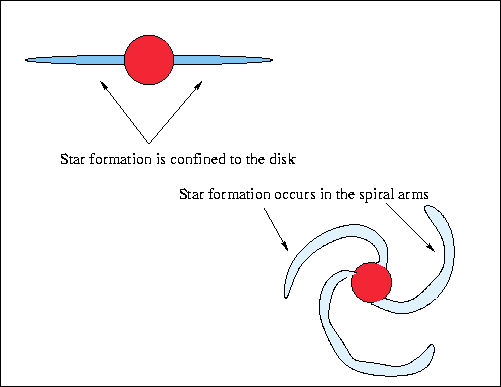
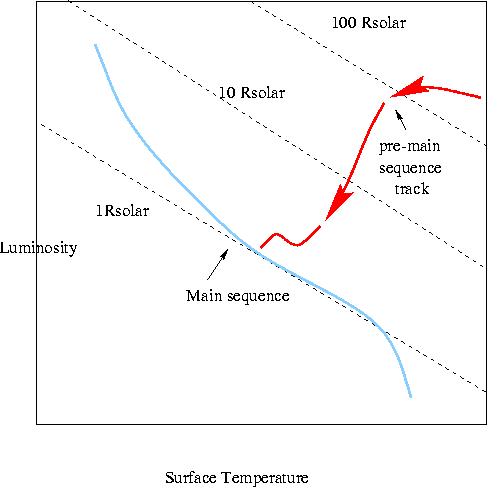
- If there was any angular momentum in the original cloud (and there was
some for sure) then as the cloud contracts it spins more rapidly just like
Tonya Harding when she pulls her arms in while spinning on the ice. This
throws some material out in a disk.
Such disks have been predicted for a long time and there was indirect
evidence for their existence. Disks around stars are crucial for the formation
of planetary systems. As we will see in a little bit, such disks are now
observed directly.
- The gravitational collapse stops when the temperature in the core of
the cloud reaches H-fusion temperatures. Now, with this extra heat source
gravity can no longer win the battle and hydrostatic equilibrium is
achieved. Exactly what central temperature this occurs at is dependent on the
mass of the final star.
- The whole process takes around 10 million years from initiation of the
collapse to the star settling on the Main Sequence.
- Q. Why are there upper and lower limits to the mass of Main-Sequence
stars?
- The upper limit of around 80 MSun is simply due to the pressure of photons. At very high luminosity,
the photons literally blow the outer layers of the star off.
- The lower limit is set by the initial GPE of a collapsing cloud
and resulting central temperature at the main sequence. Below about 0.08 MSun, the central temperature of
the collapsed object never reaches the 107 K required for starting the fusion fires and the object never
reaches stardom - these objects are called brown dwarfs.
- All the above is star formation theory that was very difficult to check
out with observations.
Two things changed this: Infrared detectors and the Hubble Space
Telescope. There have also been a few surprises resulting from the
observations of the past 10 years.
- Infrared Observations
There are two reasons the observations at wavelengths between 10 microns
and 2 microns are important.
- Protostars and proto-stellar clouds are cool and emit much of their
radiation a long wavelengths.
- Dust absorbs Blue light very effectively, Red light less
effectively and Infrared light not very effectively at all (this has
to do with the size of the dust grains in relation to the wavelength of the
E-M radiation). So, observations in the IR can "see" much further through
the dark clouds where star formation is going on.
- The Hubble Space Telescope
There is a funny thing that has to do with the apparent size of protostars
and proto-stellar disks. The nearest star formation regions are a few 100
parsecs distance. If there was a disk around a star that was about the size of
the solar system, at the distance of the nearest star formation regions its
apparent size would be about 0.1 arcsecs. This would never be "resolved"
from the ground because the atmosphere blurs images to about 1 arcsec. But,
HST has the possibility of directly observing protostars and their disks.
And it has observed them.
- The Effects of Stars on their Surroundings: It has long been known
that once stars (particularly massive stars that are very hot and produce lots
of UV photons) are formed, they have a dramatic effect on the gas and dust
around them. The best signpost for star formation regions are so-called
HII regions. "HII" stands for ionized hydrogen. Once a massive star
is formed it evaporates the remaining gas/dust cloud around it and starts
bombarding the surrounding regions with UV photons with sufficient energy to
knock the electron free of the hydrogen atoms. When the e- recombines with another H atom, the e- cascades down through the energy levels and the atom emits several
photons. The most commonly emitted photon is the one when the e- drops from the 2nd excited
level to the 1st - this is the "Hα" line in the red part of the spectrum.

- The Surprise: On unexpected thing about star formation that has
been emerging in the last decade is that is seems to be a very violent affair.
Star formation regions are full of Herbig-Haro objects like
interstellar bullets, Bi-polar outflows, energetic jets and
strong interstellar shocks. The source of energy for many of these
phenomena remains a mystery.